If you’re running Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) or Oracle Autonomous AI Database, you’ve got a configurable GraphQL server ready to query your data.
GraphQL is a strongly typed query language and runtime for APIs that lets clients request exactly the data they need through a single endpoint, reducing over- and under-fetching.
In this article, we’ll walk through using ORDS as a GraphQL server by example, including ORDS server setup.
Setup ORDS + Oracle AI Database
If you don’t have an ORDS setup available for testing, there are two easy (and free) ways you can follow along:
- If you have docker-compose on your system, download my ORDS + Oracle AI Database Free docker-compose script from GitHub. This script simultaneously starts a database container and an ORDS container with a preconfigured ORDS user.
- Spin up an instance of Oracle Autonomous AI Database in Oracle Cloud’s Always-Free tier, which includes ORDS out-of-the-box.
In this article, I’ll be using the ORDS + Oracle DB docker-compose script, but any GraalVM installation of ORDS will work.

Create a schema for GraphQL
If you’re using the docker-compose script, you can login and run this script using sql:
sql testuser/testpwd@localhost:1555/freepdb1
Let’s create a simple relational schema to query over GraphQL. Our schema involves customers, products, and orders, where each order corresponds to a specific customer and product:
-- Customers
CREATE TABLE customers (
customer_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
email VARCHAR2(320) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
full_name VARCHAR2(200) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT SYSTIMESTAMP NOT NULL
);
-- Products
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR2(200) NOT NULL,
sku VARCHAR2(64) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
price NUMBER(10,2) NOT NULL CHECK (price >= 0)
);
-- Orders (single product per order to keep 3 tables total)
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id NUMBER NOT NULL,
product_id NUMBER NOT NULL,
quantity NUMBER(6) DEFAULT 1 NOT NULL CHECK (quantity > 0),
status VARCHAR2(20) DEFAULT 'NEW' NOT NULL
CHECK (status IN ('NEW','PAID','SHIPPED','CANCELLED')),
order_ts TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT SYSTIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT fk_orders_customer FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES customers(customer_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_orders_product FOREIGN KEY (product_id) REFERENCES products(product_id)
); Then, let’s populate the tables with some sample data:
-- customers
INSERT INTO customers (email, full_name) VALUES ('ada@example.com', 'Ada Lovelace');
INSERT INTO customers (email, full_name) VALUES ('grace@example.com', 'Grace Hopper');
-- products
INSERT INTO products (name, sku, price) VALUES ('Computer', 'CPU-001', 49.99);
INSERT INTO products (name, sku, price) VALUES ('Compiler', 'A-0', 19.50);
-- orders
INSERT INTO orders (customer_id, product_id, quantity, status)
SELECT c.customer_id, p.product_id, 1, 'NEW'
FROM customers c
JOIN products p ON p.sku = 'A-0'
WHERE c.email = 'grace@example.com';
INSERT INTO orders (customer_id, product_id, quantity, status)
SELECT c.customer_id, p.product_id, 1, 'NEW'
FROM customers c
JOIN products p ON p.sku = 'CPU-001'
WHERE c.email = 'ada@example.com'; Enable the schema and objects for ORDS
Any ORDS REST-Enabled table or view of an enabled schema can be accessed through GraphQL queries. We use the ORDS PL/SQL package to enable objects and schemas
From the user schema, use the ORDS.ENABLE_SCHEMA and ORDS.ENABLE_OBJECT procedures to enable REST:
-- If you're using a schema other than 'TESTUSER', you will
-- need to change the schema name.
begin
-- using schema defaults
-- run with parameters to customize schema and base path
ords.enable_schema();
-- map CUSTOMERS table to /CUSTOMERS
ords.enable_object(
p_enabled => TRUE,
p_schema => 'TESTUSER',
p_object_type => 'TABLE',
p_object => 'CUSTOMERS',
p_object_alias => 'CUSTOMERS'
);
-- map ORDERS table to /ORDERS
ords.enable_object(
p_enabled => TRUE,
p_schema => 'TESTUSER',
p_object_type => 'TABLE',
p_object => 'ORDERS',
p_object_alias => 'ORDERS'
);
-- map PRODUCTS table to /PRODUCTS
ords.enable_object(
p_enabled => TRUE,
p_schema => 'TESTUSER',
p_object_type => 'TABLE',
p_object => 'PRODUCTS',
p_object_alias => 'PRODUCTS'
);
commit;
end;
/Query the schema with GraphQL
The GraphQL URL for the docker-compose setup is http://localhost:8888/ords/testuser/_/graphql. If you’re using Autonomous AI Database, you can find the ORDS URL in the OCI console – suffix this with /<SCHEMA/_/graphql to get the GraphQL URL.
curl http://localhost:8888/ords/testuser/_/graphql \
--user 'testuser:testpwd' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"query": "{customers { customer_id full_name }}"
}'The JSON response should look similar to the following:
{
"data": {
"customers": [
{
"customer_id": 1,
"full_name": "Ada Lovelace"
},
{
"customer_id": 2,
"full_name": "Grace Hopper"
}
]
}
}Let’s try using a variable filter to get only one customer’s data:
curl http://localhost:8888/ords/testuser/_/graphql \
--user 'testuser:testpwd' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"query": "query Customers($name: String){ customers(where: { full_name: { eq: $name }}) {full_name }}",
"operationName": "Customers",
"variables": { "name": "Ada Lovelace" }
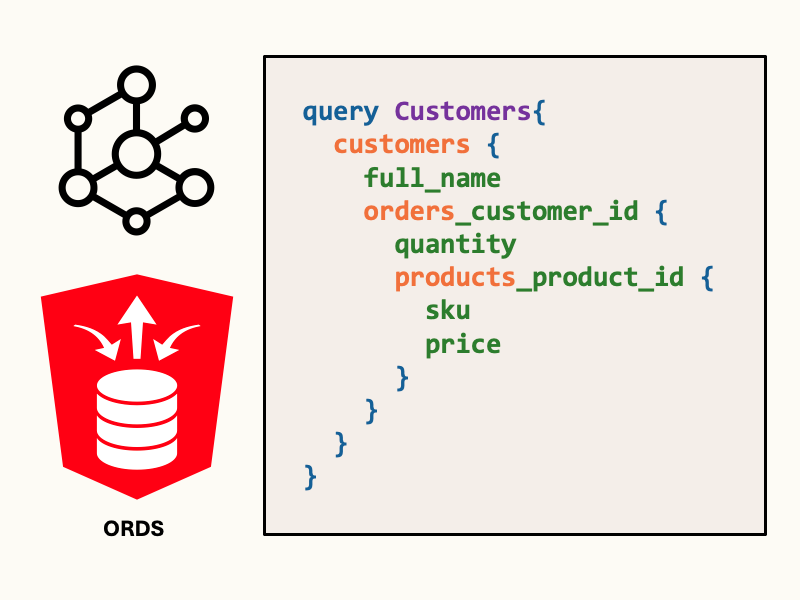
}'Now, let’s compose a query that retrieves data from multiple related tables. The following query retrieves each customer with their associated orders and products:
curl http://localhost:8888/ords/testuser/_/graphql \
--user 'testuser:testpwd' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"query": "query Customers{ customers{ full_name orders_customer_id { quantity products_product_id { sku price } } } }"
}'When this query is run on the database, JOIN operations occur server side. The combined customers-orders-products data is assembled into JSON, and passed back to the user.
ORDS GraphQL capabilities also support advanced filtering, sorting, nesting and pagination. Refer to the ORDS GraphQL documentation for additional samples.
References
- Custom ORDS installation with GraalVM and GraphQL <- read this if you want to install ORDS standalone, without Autonomous AI Database or the container image
- ORDS enable schema
- GraphQL in ORDS documentation
- GraphQL() function in Oracle SQL
Leave a Reply